inceptionTime 구현하기
InceptionTime: Finding AlexNet for Time Series Classification 논문의 모델 직접 구현해보기
- 조건:
- 공개된 모델 코드 확인하지 않고, 논문을 위주로 구현
- Pytorch 기반으로 구현
- 인터넷 검색 허용
- 생성형 AI 사용 지양
- 검색 내용 기록하기
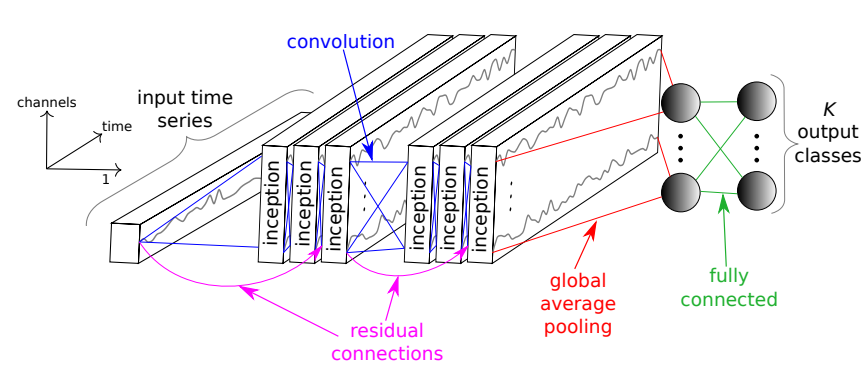
모델 아키텍처
InceptionTime
- 랜덤 초기화된 서로 다른 $5$개의 Inception network 로 구성된 앙상블
- 시계열 데이터에 Receptive Field 개념 도입
Inception Network
- $2$개의 서로 다른 residual block 으로 구성
- residual block은 $3$개의 Inception module 으로 구성
- residual block의 입력은 shortcut linear connection을 통해 다음 block의 입력으로 전달
- vanishing gradient problem 해소
- residual block의 입력은 shortcut linear connection을 통해 다음 block의 입력으로 전달
- residual block 가장 마지막에 Global Average Pooling(GAP) layer로 전체 시간 차원의 multivariate time series(MTS)에 대해 평균
- 마지막으로 클래스 개수만큼의 뉴런을 가진 softmax 층으로 구성
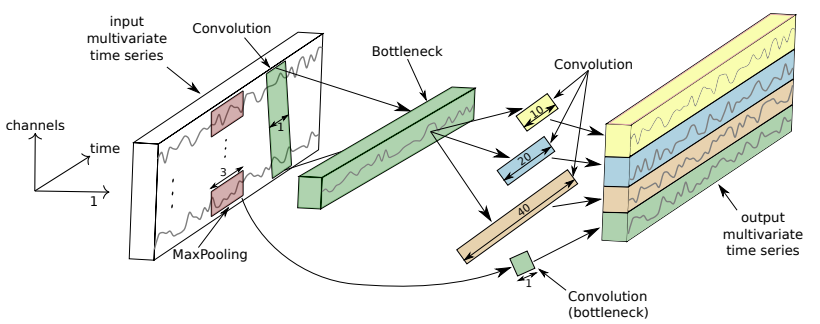
Inception Module
입력이 $M$ 차원의 MTS라고 가정
- bottleneck layer
- 길이 $1$, stride $1$인 필터 $m$개 적용(\(m \ll M\))
- 차원과 모델 복잡도 감소
- 작은 데이터에 대한 overfitting 문제 해소
- 필터의 길이를 길게 설정할 수 있게 됨
- 길이 $1$, stride $1$인 필터 $m$개 적용(\(m \ll M\))
- multiple filters of different lengths
- 동일한 입력 시계열에 길이가 서로 다른 필터를 동시에 적용
- MaxPooling operation
- 사소한 잡음 무시하기 위해 도입
TSC 앙상블
$5$개의 Inception network로 구성된 앙상블
- 각 network의 예측에 동일한 비중 부여
- 개별 network의 불안정성을 앙상블을 통해 활용하여 전체 성능을 향상
서로 다른 초기화로 생성된 네트워크의 예측을 앙상블하는 방법:
\[\hat{y}_{i,c} = \frac{1}{n} \sum^{n}_{j=1} \sigma_{c} (x_{i}, \theta_{j}) | \forall c \in [1, \text{C}]\]Receptive field
- 특정 뉴런이 반응하는 입력 공간(이미지, 시계열 등)의 일부
- 주어진 뉴런의 활성화에 입력 데이터가 얼마나 영향을 미치는지를 결정
- 시간 데이터의 경우, RF는 신경망의 최대 시야를 측정하는 이론적 값으로 간주될 수 있음
- RF가 클수록 더 긴 패턴을 감지하는 데 (이론적으로) 더 유리
시계열 데이터의 RF를 계산하는 공식(stride=1):
\[\text{RF} = 1 + \sum_{i=1}^{d} (k_i - 1)\]여기서 $d $는 네트워크의 깊이, $ k_i$는 각 층의 필터 길이
- 층을 추가하면 RF가 약간 증가하며, 필터 길이를 늘리면 RF가 크게 증가함
- 컴퓨터 비전에서 더 큰 RF가 더 많은 컨텍스트를 캡처하는 데 필요하다는 점을 고려하여, 긴 1차원 시계열 데이터에서 더 큰 패턴을 감지하려면 더 큰 RF가 필요하다고 가정
모델 구현
입력 샘플
1
2
3
4
5
batch = 5
in_channels = 10
time = 20
input_mts = torch.randn(batch, in_channels, time)
input_mts.shape
InceptionModule
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
class InceptionModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
in_channels: int,
bottleneck_channels: int,
kernel_sizes: list[int],
maxpool_kernel_size: int = 3
):
super(InceptionModule, self).__init__()
self.bottleneck = nn.Conv1d(in_channels, bottleneck_channels, 1)
self.conv_layers = [nn.Conv1d(bottleneck_channels, bottleneck_channels, kernel_size, padding='same') for kernel_size in kernel_sizes]
self.max_pool = nn.MaxPool1d(maxpool_kernel_size , 1, maxpool_kernel_size//2)
init.xavier_uniform_(self.bottleneck.weight)
for conv_layer in self.conv_layers:
init.xavier_uniform_(conv_layer.weight)
def forward(self, x):
# bottleneck
x_ = self.bottleneck(x)
bottleneck_output = torch.cat([conv_layer(x_) for conv_layer in self.conv_layers], 1)
# max pooling
max_pooling_output = self.bottleneck(self.max_pool(x))
x = torch.cat([bottleneck_output, max_pooling_output], 1)
return nn.functional.relu(x)
Residual Block
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
class ResidualBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
in_channels: int,
bottleneck_channels: int,
kernel_sizes: list[int],
maxpool_kernel_size: int = 3
):
super(ResidualBlock, self).__init__()
output_size = (len(kernel_sizes) + 1) * bottleneck_channels
self.inception_module1 = InceptionModule(in_channels, bottleneck_channels, kernel_sizes, maxpool_kernel_size)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv1d(output_size, in_channels, 1)
self.inception_module2 = InceptionModule(in_channels, bottleneck_channels, kernel_sizes, maxpool_kernel_size)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv1d(output_size, in_channels, 1)
self.inception_module3 = InceptionModule(in_channels, bottleneck_channels, kernel_sizes, maxpool_kernel_size)
init.xavier_uniform_(self.conv1.weight)
init.xavier_uniform_(self.conv2.weight)
def forward(self, x):
x_ = self.inception_module1(x)
x_ = self.conv1(x_)
x_ = self.inception_module2(x_)
x_ = self.conv2(x_)
x_ = self.inception_module3(x_ + x)
return x_
모델 아키텍처 이미지를 토대로 residual connection 구현
InceptionTime
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
class InceptionTime(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
in_channels: int,
bottleneck_channels: int,
kernel_sizes: list[int],
n_classes: int,
maxpool_kernel_size: int = 3
):
super(InceptionTime, self).__init__()
self.output_size = (len(kernel_sizes) + 1) * bottleneck_channels
self.residual_block1 = ResidualBlock(in_channels, bottleneck_channels, kernel_sizes, maxpool_kernel_size)
self.conv = nn.Conv1d(self.output_size, self.output_size, 1)
self.residual_block2 = ResidualBlock(self.output_size, bottleneck_channels, kernel_sizes, maxpool_kernel_size)
self.gap = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool1d(1)
self.fc = nn.Linear(self.output_size, n_classes)
self.softmax = torch.nn.Softmax(-1)
init.xavier_uniform_(self.conv.weight)
init.xavier_uniform_(self.fc.weight)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.residual_block1(x)
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.residual_block2(x)
x = self.gap(x)
x = torch.reshape(x, (-1, self.output_size))
x = self.fc(x)
x = self.softmax(x)
return x
검색 기록
- https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/introyt/modelsyt_tutorial.html
- https://docs.python.org/3/library/typing.html
- https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Conv1d.html
- https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.MaxPool1d.html
- https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.cat.html
- https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.AvgPool1d.html
- https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.AdaptiveAvgPool1d.html
- https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Linear.html#torch.nn.Linear
- https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.reshape.html
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/49433936/how-do-i-initialize-weights-in-pytorch
- https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.init.html#torch.nn.init.xavier_uniform_
- https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Softmax.html
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.